Combining the strengths of both Xenics and Telops technologies in the field of infrared imaging and camera systems lead to innovative and powerful solutions.
We would like to share our infrared technology knowledge with you, such that together we can find new and interesting infrared applications.
- Exploring the Advantages of Reflected Light Imaging, read more about Shortwave Infrared technology
- The Advantages of Midwave Infrared (MWIR) Thermal Imaging, read more about Midwave Infrared technology
- Exploring Longwave Infrared (LWIR) Technology and its Thermal Imaging Advantages, read more about Longwave Infrared technology
On this page you find more information about infrared as a technology, its history, infrared detectors and an infrared glossary.
Infrared as a technology
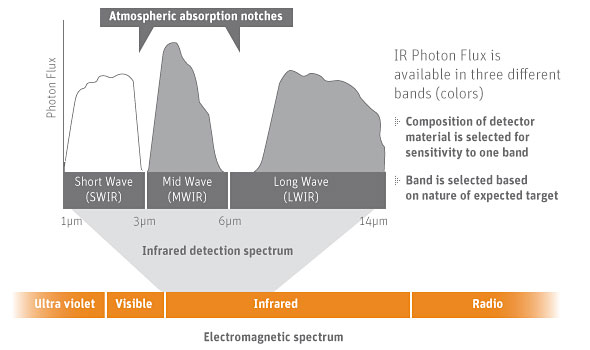
As the Latin prefix “infra” means “below” or “beneath”, “infrared” refers to the region beyond or beneath the red end of the visible color spectrum. The infrared region is located between the visible and microwave regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. All objects radiate some energy in the infrared, even objects at room temperature and frozen objects such as ice. Therefore infrared is often referred to as the heat region of the spectrum.
History of Infrared Detectors
The history of infrared started in the 19th century. In these days, the development of infrared detectors was mainly focused on thermometers and bolometers. Photon detectors were only developed in the 1940’s and improved the sensitivity and response time. During the 1940’s and 50’s new materials were developed for IR sensing, of which the semiconductor alloys of chemical table group III-V, IV-VI and II-VI were the most important ones. These alloys allowed the bandgap of the semiconductor to be custom tailored for a specific application.
In the late 1960’s and early 1970’s, “first generation” linear arrays were developed. In the meantime Charge Coupled Devices (CCDs) were invented which made it possible to envision “second generation” detector arrays. These were eventually born in the 1990’s and provided large 2D arrays and linear arrays with square and rectangular pixels.


Infrared Detector Types
An infrared detector is simply a transducer of radiant energy, converting radiant energy in the infrared into a measurable form. Infrared detectors can be used for a variety of applications in the military, scientific, industrial, medical, security and automotive arenas. They are available as single element detectors in circular, rectangular, cruciform, and other geometries. As linear arrays, and as 2D focal plane arrays.
Infrared detectors can be made from many compound semiconductors, each with its own characteristics.
Infrared Glossary
The infrared world is a high-tech world with a lot of typical infrared jargon. Here you can find an overview of some of the most recurring terms. Next to this infrared dictionary, you can also find a list of infrared acronyms.





